Type: GitHub Repository Original Link: https://github.com/FareedKhan-dev/qwen3-MoE-from-scratch Publication Date: 2025-09-20
Summary #
WHAT - This is a tutorial that guides you through building a Qwen 3 MoE (Mixture-of-Experts) model from scratch, using Jupyter Notebook. The tutorial is based on a Medium article and includes a GitHub repository with code and additional resources.
WHY - It is relevant for AI business because it provides a practical guide to implementing an advanced LLM (Large Language Model) that can be used to enhance natural language processing capabilities. This can lead to more efficient and specialized solutions for AI applications.
WHO - The main actors include Fareed Khan, author of the tutorial, and Alibaba, which developed the Qwen 3 model. The primary audience is the community of AI developers and researchers.
WHERE - It positions itself in the AI educational market, offering resources for the development of advanced LLM models. It is part of the open-source tools ecosystem for AI.
WHEN - The tutorial was published in 2025, indicating that it is based on recent and advanced technologies. The maturity of the content is linked to the spread and adoption of the Qwen 3 model.
BUSINESS IMPACT:
- Opportunities: Implementing MoE models can improve the efficiency and specialization of AI solutions, offering a competitive advantage.
- Risks: Dependence on open-source technologies can involve risks related to code maintenance and updates.
- Integration: The tutorial can be used to train the internal development team, integrating the acquired knowledge into the existing technological stack.
TECHNICAL SUMMARY:
- Core technology stack: Jupyter Notebook, Python, PyTorch, Hugging Face Hub, sentencepiece, tiktoken, torch, matplotlib, tokenizers, safetensors.
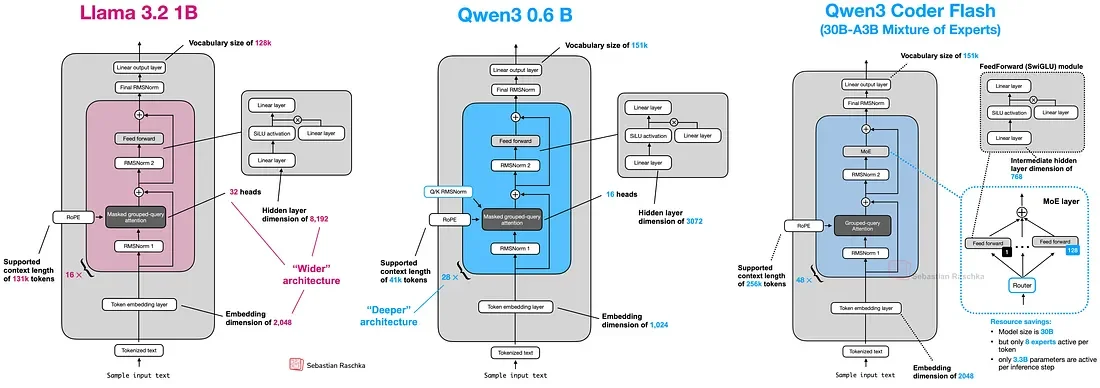
- Scalability and architectural limits: The described model has 0.8 billion parameters, much fewer than the 235 billion of the original Qwen 3 model. This makes it more manageable but also less powerful.
- Key technical differentiators: Use of Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to activate only part of the parameters for queries, improving efficiency without sacrificing performance. Implementation of advanced techniques such as Grouped-Query Attention (GQA) and RoPE (Rotary Position Embedding).
Use Cases #
- Private AI Stack: Integration into proprietary pipelines
- Client Solutions: Implementation for client projects
- Development Acceleration: Reduction of project time-to-market
- Strategic Intelligence: Input for technological roadmap
- Competitive Analysis: Monitoring AI ecosystem
Resources #
Original Links #
Article recommended and selected by the Human Technology eXcellence team, processed through artificial intelligence (in this case with LLM HTX-EU-Mistral3.1Small) on 2025-09-23 16:51 Original source: https://github.com/FareedKhan-dev/qwen3-MoE-from-scratch
Related Articles #
- AI Engineering Hub - Open Source, AI, LLM
- Introducing Qwen3-Max-Preview (Instruct) - AI, Foundation Model
- How to Segment Videos with Segment Anything 3 (SAM3) - JavaScript, Java