Type: Web Article Original link: https://www.krupadave.com/articles/everything-about-transformers?x=v3 Publication date: 2024-01-15
Summary #
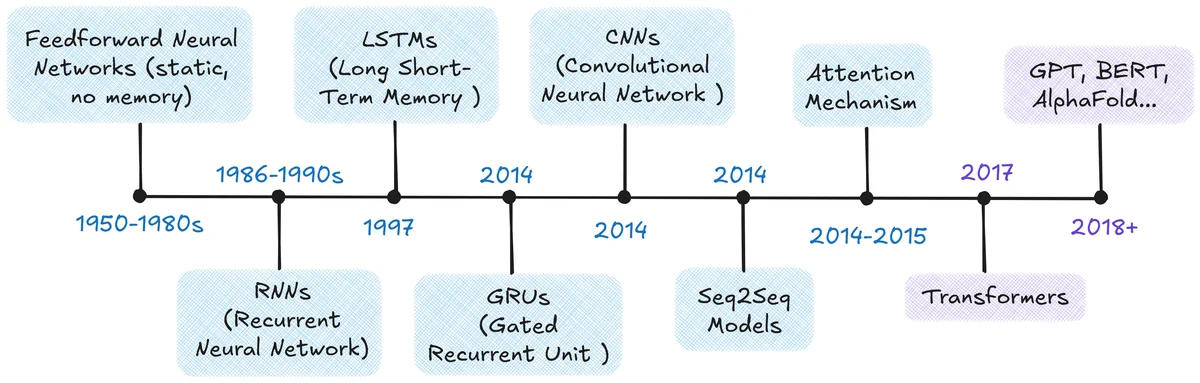
WHAT - This article discusses the history and functioning of the transformer architecture, a fundamental deep learning model for natural language processing (NLP). It provides a visual and intuitive explanation of the evolution of language models, from the use of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to modern transformers.
WHY - It is relevant for AI business because transformers are the foundation of many advanced NLP models, such as BERT and GPT. Understanding their operation and evolution is crucial for developing new competitive AI solutions.
WHO - The author is Krupa Dave, an expert in the field of AI. The article is published on Dave’s personal website, which is aimed at a technical audience interested in AI and machine learning.
WHERE - It is positioned in the market for technical education and scientific dissemination in the field of AI. It is useful for professionals and researchers who want to deepen their understanding of transformers.
WHEN - The article was published on January 15, 2024, reflecting current knowledge and recent trends in the field of AI.
BUSINESS IMPACT:
- Opportunities: Provides a solid foundation for the development of new NLP models, improving internal competence on transformer architecture.
- Risks: Does not represent a direct risk, but ignoring the innovations described could lead to a competitive delay.
- Integration: Can be used to train the technical team, improving innovation capacity and the development of new AI products.
TECHNICAL SUMMARY:
- Core technology stack: The article discusses the transformer architecture, including encoder, decoder, attention mechanisms (self-attention, cross-attention, masked self-attention, multi-head attention), feed-forward networks, layer normalization, positional encoding, and residual connections.
- Scalability and architectural limits: Transformers are known for their ability to scale effectively, allowing the processing of data sequences in parallel. However, they require significant computational resources.
- Key technical differentiators: The use of attention as the main mechanism for processing data sequences, allowing greater flexibility and precision compared to previous models.
Use Cases #
- Private AI Stack: Integration into proprietary pipelines
- Client Solutions: Implementation for client projects
- Strategic Intelligence: Input for technological roadmap
- Competitive Analysis: Monitoring AI ecosystem
Resources #
Original Links #
- Everything About Transformers - Original link
Article recommended and selected by the Human Technology eXcellence team, processed through artificial intelligence (in this case with LLM HTX-EU-Mistral3.1Small) on 2025-10-31 07:33 Original source: https://www.krupadave.com/articles/everything-about-transformers?x=v3
Related Articles #
- A foundation model to predict and capture human cognition | Nature - Go, Foundation Model, Natural Language Processing
- Token & Token Usage | DeepSeek API Docs - Natural Language Processing, Foundation Model
- Stanford’s ALL FREE Courses [2024 & 2025] ❯ CS230 - Deep Learni… - LLM, Transformer, Deep Learning